CORPORATE LAWS
ECB 2 Returns for the month of May 2021 to be filed on or before 7 June 2021
MCA has vide General Circular No 06/2021 dated 03/05/2021 has given additional time till 31 July 2021, filing of certain forms which were due for filing between 1 April 2021 and 31 May 2021 without any additional filing fees.
MCA has vide General Circular No 07/2021 dated 03/05/2021, provided for additional time for filing of forms related to creation or modification of charge where creation/modification of charge date is prior to 1 April 2021 and timeline for such filing has expired and where creation/modification of charge falls on any date between 1 April 2021 to 31 May 2021.
As per MCA’s General Circular No. 08/2021 dated 03/05/2021, the time gap between two Board Meetings has been extended to 180 days from 120 days for the first two quarters of the Financial Year 2021-22. This will give additional time to Companies in India to comply with the holding of a Board Meeting.
DIRECT TAX
Circulars/Notifications/Press Release
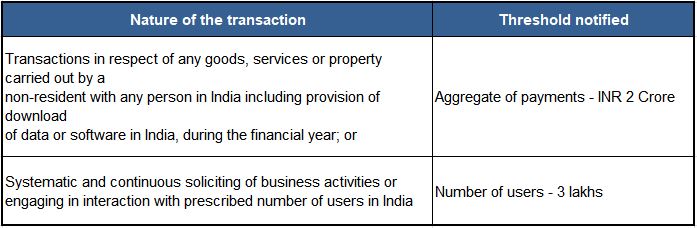
CBDT Notifies threshold for Significant Economic Presence with effect from 01 April 2022
Notification 41/2021 dated 03 May 2021
- Government of India has now notified thresholds (i.e. payment and user thresholds) for Significant Economic Presence (SEP) to constitute ‘business connection’ (a concept similar to ‘Permanent Establishment’ under tax treaties) in India. Broadly, the scope of ‘business connection’ was expanded to include SEP of a non-resident in India with an intent to tax non-residents operating digitised businesses in India (which function without a physical presence)
Relaxation to Medical facilities providing Covid treatment for receiving cash of ₹ 2 Lakh or more
Notification No. 56/2021 and 59/2021 dated 07 May 2021 and 10 May 2021 respectively
CBDT has specified that hospitals, dispensaries and other similar medical facilities providing COVID treatment can accept payments in cash for ₹ 2 Lakhs and more.
This relaxation is provided during 01 April 2021 to 31 May 2021, and is available upon the medical facilities obtaining the PAN or Aadhar of the patient and the payer and the relationship between them.
CBDT notifies, Rules for computation of Capital Asset for Sec 50B-Slump Sale
Rule 11UAE – Provides for higher of below values as consideration:
• FMV 1 shall be determined as below:
A+B+C+D – L where,
A = book value of assets not covered under B,C and D and tax effects.
B = value of jewellery / artistic work as per valuation report
C = fair value of shares / securities as per Rule 11UA
D = stamp duty value of immovable properties
L = book value of external liabilities apart from tax effects and ascertained provisions.
• FMV 2 shall be determined as below:
E+F+G+H where,
E = monetary consideration received for assets covered in slump sale
F, G and H = non-monetary consideration equal to corresponding values of assets mentioned in B, C and D respectively.
CBDT gives clarification for extension of time limits for filing CIT(Appeals)
Circular No.10/2021, dated 25 May 2021
- Clarification has been given for circular issued on 30 April, 2021 and order by the Supreme Court on 27 April, 2021 for extension of time limits for filing the appeals before (CIT) Appeals.
- It is clarified that if different relaxations are available to the taxpayers for a particular compliance, taxpayer is entitled to choose that relaxation which is more beneficial to him.
- Hence, time limit to file an appeal before the CIT(A) is covered by the above and consequently stands extended till further notice.
Case Laws
ITAT: Deletes addition of share premium u/s 68 for newly operational company; Finds business activities justifiable
DCIT vs Mahalaxmi TMT Pvt. Ltd. dated 19 April 2021
- Assessee engaged in business of iron and steel established itself in FY 2004-05 and commenced its operations in AY 2010-11.
- In AY 2010-11, Assessee issues shares at a premium and received ₹37 Cr.
- Revenue treated it as unexplained cash credit u/s 68 contending-
♦ Issue of shares at premium not justified owing to no business activity performed,
♦ Company invested in Assessee were loss making. ITAT highlighted that-
♦ Assessee has submitted documents like bank statement, MOA AOA etc for identity of investors and their credit worthiness
♦ Transaction has been carried out through proper banking channelTherefore, ITAT rules in favour of assessee stating that assessee discharged its onus u/s 68 satisfactorily to obviate the mischief of this section.
Delhi HC : Order passed before expiry of time allowed in SCN
BL Gupta Construction (P) Ltd Vs. National e-Assessment Centre - [2021]
- Assessee was in construction business. On 18 March 21, assessee was served a SCN by National e-Assessment centre (NeAC) to respond to a draft assessment order.
- Time period allowed to respond in SCN was 26 March 21.
- However, before expiry of time allowed in SCN, NeAC passed final assessment order along with Notice of demand and Notice for imposition of penalty.
- Aggrieved by this, assessee filed appeal before the Delhi High Court. The High Court ruled in favour of assessee stating that there had been a breach of Principles of Natural justice on part of NeAC.
- Accordingly, HC granted interim stay on Notice of demand u/s 271AAC(1).
Input service tax written off is an allowable expenditure u/s 37 (1)
FIH India (P.) Ltd. Vs DCIT, Chennai
- The assessing officer has disallowed the expenditure of the input service tax written off in the books of accounts on three objections:
♦ The expenditure is not a deductible expenditure u/s 37(1), because the same is not routed through profit and loss.
♦ The same is never treated as income at any point in time.
♦ The same is related to previous year and hence a prior period expenditure , not eligible to be claimed this year. On which, ITAT held that:
♦ If assessee had adjusted the input tax credit on output services, then it can not again claim as deduction and then AO had not
disputed that service tax paid on input services was not debited in profit and loss account. Hence there is no merit in the first
objection.♦ The assessee has paid service tax on the input services and hence when any taxes paid on purchase or services is a part of cost
of goods or services which can be either debited to profit and loss account if the credit not availed or if the credit is availed, the tax
portion taken out of profit and loss treated as part of current asset.
♦ Although part of the credit pertains to last year , it is carried forward to subsequent financial year as per the provisions of law.Also, in the case of CIT vs Kaypee Mechanical (P) Ltd. And Girdhar Fibres (P.) Ltd. Vs. ACIT has held that it is an item allowable as deduction u/s 37(1).
Chandigarh ITAT: Sec. 11 exemption cannot be denied just because assessee failed to file audit report along with ITR
Sanskriti KMV School Vs. CIT
- Assessee company is public school imparting education and affiliated to CBSE. The school was claiming exemption for the AY 2013-14, 2014-15 and 2015-16.
- The AO denied the exemption on the grounds that it does not solely exist for education purpose and hence not eligible for exemption, however CIT(A) reversed the order of AO in all the three preceding years and accepted the exemption claim.
- In the concerned year, AO again disallowed the exemption on the basis that assessee fails to prove that it exists solely for the purpose of education and not for profit and also, that it has not filed that audit report in form 10BB along with the return.
- Aggrieved which Assessee had filed the appeal with CIT (A) and it rejected the claim despite the earlier year’s order of ITAT.
- ITAT held that this finding of CIT(A) is contemptuous of not following the order of her predecessor for earlier years which is duly confirmed with the ITAT. Second, various high courts have consistently given a finding that filing of audit report is not mandatory, it is only directory and can be filed to claim exemption or deduction at the time of proceeding or even appellant proceedings.
Delhi HC: Grants stay on writ petition filed against faceless assessment order passed without SCN cum draft order
Globe Capital Foundation Vs National E-assessment centre, dated 13 May 2021
- Delhi HC issues notice on writ petition seeking a stay on the assessment order passed by National E-assessment Centre under Faceless Assessment Scheme in violation of principles of natural justice.
- Considers assessee’s submission that assessee was not issued a show cause notice-cum-draft assessment order as mandated under the scheme and the final assessment order was passed u/s 143(3) read with section 144B; Lists the matter for hearing on 30 July 2021 and grants stay on the operation of the assessment order;
Vishakhapatnam ITAT: Finds enhanced jewellery sales on demonetization date as genuine; Deletes Sec. 68 addition
M/s Hirapanna Jewellers Vs ACIT, dated 12 May 2021
- Assessee-firm Hirapanna Jewellers, engaged in the trading of jewellery, deposited ₹5.72 Cr., post demonetization, in high denomination notes and justified its source as enhanced cash sales of ₹4.72 on 08 November 2016 due to panic buying by the public.
- Based on survey conducted in Assessee’s premises u/s 133A by DDIT(Inv), the Assessee could not provide CCTV footage, KYC or personal details of buyers, justification of mismatch of average sales when compared to these sales in 4 hours.
- AO conducted another survey and finally made addition of ₹4.72 Cr u/s 68 read with section. 115BBE and taxed the same @ 60%.
- On Revenue appeal, ITAT deleted addition u/s 68 stating that once purchase/ sales matches with inflow/ outflow of stock, the transaction cannot be doubted. ITAT finds force in the Assessee’s submission that due to demonetization, the public panicked as the cash available with them in old denomination notes became illegal from 09 November 2016, leading to investment in jewellery
Mumbai ITAT: Forex Gains on repayment of loan given to NR relative, non-taxable as capital receipt
Aditya Balkrishna Shroff Vs.ITO, dated 17 May 2021
- Mumbai ITAT, allows Assessee’s appeal ex parte, and holds addition made in the hands of assessee-individual on account of forex gains for AY 2013-14 arising from repayment personal forex loan as capital receipt not chargeable to tax;
- Assessee extended a personal interest-free loan of USD 200,000 (equivalent to ₹90 Lacs) to his cousin in Singapore under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) of RBI and received ₹1.12 Cr. as the repayment thereof;
- ITAT observes that the said loan was given on capital account and was not given in the course of business of the assessee and the accretion of money, in rupee terms, was on account of increase in the value of the US Dollars advanced as a capital transaction;
- Opines that Revenue erred in “putting the cart before the horse” by deciding the head under which the income is to be taxed without even deciding whether it is in the nature of income or not, and by mixing up the concept of ‘income’ with the concept of ‘gains’;
Delhi ITAT: Deletes TP adjustment on export commission and royalty.
Honda Motorcycle & Scooter India Pvt Ltd Vs. DCIT, dated 21 May 2021
- Facts: Assessee has challenged rejection of TNMM adopted for benchmarking its international transaction.
- Assessee paid export commission to its AE in Japan to access international markets and AE’s distribution network and royalty for technical know-how.
- TPO held that the ALP of payment of export commission and royalty on sales should be NIL as per CUP method since assessee failed to satisfy the commercial expediency or need test.
- Result : Ruling in favour of assessee relying on co-ordinate bench decisions in Assessee’s own case and stating that commercial test stands fulfilled. TP adjustments deleted.
Pune ITAT: No capital gains on unmaterialised development agreement with builder
ITO Vs. Amit Murlidhar Kamthe, dated 17 May 2021
- Facts: Assessee-Individual for AY 2008-09, was found to have entered into two development agreements with a builder and no capital gain therefrom was declared by the Assessee;
- Revenue assessed STCG and LTCG as per Sec. 53A of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 (TPA) read with section 2(47)(v). Held that parting with possession of the land in favour of the builder and receiving a part of the agreed consideration amounted to ‘transfer’.
- ITAT observes that under development agreements, the builder was allowed to enter into the property as a licensee (not owner).
- Title to land was under litigation by virtue of order under Urban Land (Ceiling & Regulation) Act, 1976 at the material time;
- Conclusion: ITAT observes agreement and ownership under UCL Act to conclude no title existed at relevant time and hence no transfer took place. Further, development agreements did not allow transfer of ownership and were further cancelled at future time. Hence, no capital gains arose.
Indore ITAT: Loans received from companies with common substantial shareholders, taxable u/s 2(22)(e)
DCIT Vs Ryder Trans International Pvt Ltd
- Facts: Loans received by one private companies from three other private companies, all having common shareholder.
- Assessee was subject to reassessment proceedings AY 2012-13 for escapement of deemed dividend u/s 2(22)(e) amounting to ₹2.2 Cr. on receipt of loan from three companies.
- ITAT relies on SC ruling in National Travel Services and holds that ‘concern’ includes a company and substantial interest includes shareholding in excess of 20 percent.
- Conclusion: Deemed dividend provisions are applicable in the present case and addition by AO upheld.
Other Updates
CBDT’s (Foreign Tax & Tax Research Division) releases International Tax Bulletin for the month of March and April 2021.
- US proposal of ‘Made in America Tax Plan’ whereby US federal corporate income tax rate would rise from 21% to 28%;
- European Union’s new reporting obligations for digital platforms-
♦ Obligation to collect and verify information in accordance with due diligence procedures, and
♦ Obligation to report information on sellers using the platform for supply of goods or services - India-Iran Tax Treaty entering into force on 1 April 2021.
- Anti-BEPS measures introduced by Canada in the Budget 2021
♦ Digital services tax
♦ Interest deduction limits – akin to Sec. 94B of Indian IT Act
♦ Plans for changing transfer pricing (TP) rules, and
♦ Plans for mandatory disclosure rules to counter BEPS related tax losses.
Goods and Services Tax
GST law amendments
GST Council in its 43rd meeting held on 28th May 2021 announced various trade facilitation measures. Few important ones are summarized below:
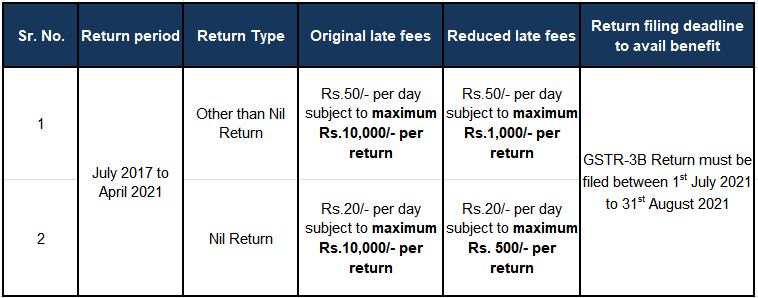
• Amnesty scheme notified to provide relief to taxpayers regarding late fees on delayed filing of GSTR-3B Return:
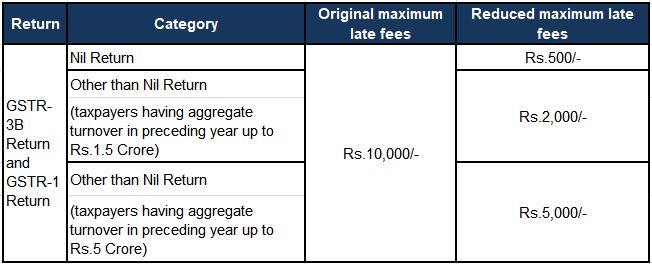
• Rationalization of late fees imposed under Section 47 of the CGST Act for small taxpayers, applicable from the tax period June 2021 or quarter ending June 2021
• Exemption from generation of E-invoice
Government department’ and “Local authority’ have been exempted from requirement of E-Invoice.
• Input tax credit matching (ITC) with GSTR-2A/2B report:
The Government has done away with the matching requirement on a monthly basis for the period April 2021 to May 2021, and for this period, taxpayer may do ITC matching with GSTR-2A/2B report cumulatively in June 2021 GSTR-3B return.
• Filing of return through EVC option:
Government allows companies to file their GST compliance returns viz. GSTR-3B return, GSTR-1 return, Invoice Furnishing Facility (IFF), through Electronic Verification Code (EVC) option till 31 August 2021.
• Relaxation for general compliance under CGST Act:
- Where time limit for completion or compliance of any action whether by tax authority or by a taxpayer is from 15-04-2021 to 29-06-2021, the due date has been extended to 30-06-2021;
- Where time limit for completion or compliance of any action for verification and approval of registration application whether by tax authority or by a taxpayer is from 15-04-2021 to 30-06-2021, the due date has been extended to 15-07-2021;
- In case where notice is issued for rejection of refund claim and where time limit for issuance of refund order is from 15-04-2021 to 29-06-2021, the due date has been extended to 30-06-2021 or 15 days after the receipt of reply to the notice, whichever is later.
- GST Council have also clarified that wherever timelines for actions have been extended by the Hon’ble Supreme Court in its suo motu writ petition, the same would prevail over aforementioned extensions
• Government notifies Section 112 of the Finance Act, 2021 from 1 June 2021
The Government has notified the amendment in Section 50 of the CGST Act with retrospective effect from 1-7-2017. The amendment provides that, interest on delayed payment of GST liability would be computed only on net tax liability paid in cash.
It is worthwhile to note that, benefit of computation of interest only on the cash component appears to be applicable only in case of delay in filing of GST returns and not in cases where tax liability is paid at the time of GST audit or in cases where GST return is already filed but few tax invoices were inadvertently missed to be reported in the return and thus, tax payment is delayed. Interest in such cases would be computed on the gross tax amount only.
• Government announces reduction in GST rates on COVID-19 relief material
The 44th Meeting of the GST Council was held via video conferencing under the Chairmanship of the Union Finance & Corporate Affairs Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman on 12th June 2021. Vide the said meeting, the GST Council has recommended certain GST rate concessions towards goods used in Covid-19 relief and management, most notably being:
• Amphotericin B (drug used for treating Black Fungus cases) – GST reduced from 5% to NIL
• Remdisivir, medical grade oxygen, oxygen concentrator/ generator, ventilators, Covid testing kits, pulse oximeters, hand sanitizer and temperature checking equipment – GST rate has been reduced to 5%
• Ambulances – GST rate has been reduced from 28% to 12% to aid in the fight against the global pandemic.
The above concessional GST rates would be in force up to 30 September 2021.
• Relaxations on import of oxygen concentrators for personal use stands rescinded:
Vide Notification No. 30/2021 –
Customs, dated 01 May 2021, IGST on import of oxygen concentrators for personal use was reduced from 28% to 12% for the period up to 30 June 2021. However, recently vide Notification No. 33/2021 – Customs, dated 14 June 2021, the Government has prospectively rescinded the said IGST concession. Thus, effective from 14 June 2021, IGST at 28% would be applicable on import of oxygen concentrators for personal use.
Interestingly, the Delhi High Court recently had an opportunity to decide on the constitutionality of levy of IGST on oxygen concentrators for personal use. On 21 May 2021, the Hon’ble High Court held that such levy of IGST is unconstitutional and a violation of the fundamental right to life. Government against this decision filed an appeal with the Hon’ble Supreme Court, which stayed the Delhi HC decision on 01 June 2021. The matter is sub judice with Hon’ble Supreme Court.
Customs update
Update on recent customs duty exemptions/benefit in support of the fight against the Covid-19 pandemic
As a part of the measure for fight against the recent upsurge in the Covid-19 pandemic, the Government has further extended customs duty exemptions/benefits to provide relief during the ongoing pandemic:
A. Basic customs duty exemption on import of Amphotericin B:
Last month, the Government notified basic customs duty exemption on the import of specified Covid-19 relief material in the fight against Covid-19 pandemic. Now, pursuant to the decisions in the 43rd Meeting of the GST Council held on 28 May 2021, the said exemption has been extended to import of Amphotericin B, which is a drug used in the treatment of Mucormycosis (Black Fungus) cases. Further, the exemption has been extended up to 31 August 2021.
B. IGST exemption on import of Covid-19 relief material extended to any importer:
In the fight against the pandemic, to augment the efforts of the State Governments, last month, IGST exemption on import of specified Covid-19 relief material has been granted to imports by State Governments/entities nominated by State Governments. Now the same exemption has been extended to other importers as well with following conditions:
- Importer category: Any entity can import the aforesaid Covid-19 relief material;
- Covid relief material: Goods imported from abroad are meant to be donated to the Central Government, various State Governments or a relief agency recommended by State authority. Such donated goods are in turn intended to be distributed free of cost in India;
- Certificate: Central Government or nodal authority [including authority appointed by a State Government] needs to furnish a certificate before clearance of goods, to effect that such goods are meant for free distribution for Covid relief;
- Compliance: Imported needs to furnish within 6 months (further extension of 3 months is possible) either of the following:
- Certificate issued by the Central or a State Government that the imported goods were received by them for free distribution; or
- A statement showing details of goods distributed free of cost duly certified by nodal authority of State Government – where imported goods are donated to any relief agency on the recommendation of the nodal authority.
The validity of this exemption to imports by State Governments as well as other importers is extended for imports up to and inclusive of 31 August 2021.
Due Dates
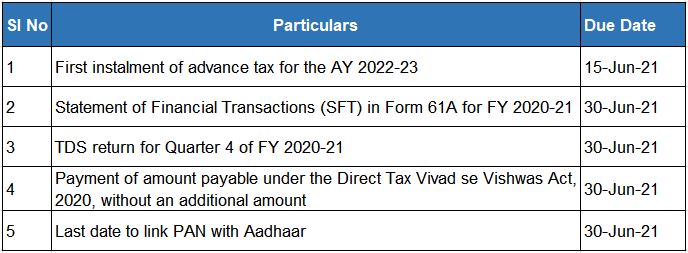
Income Tax Due Dates May 2021
GST due dates 2021
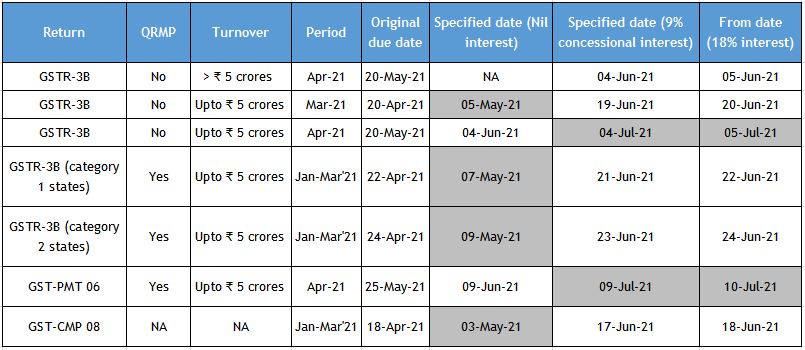
Due dates for filing GST return in the month of June 2021
With relaxation in interest rate for delay in GST payment
With relaxation in late fees for delay in filing of GST compliance returns
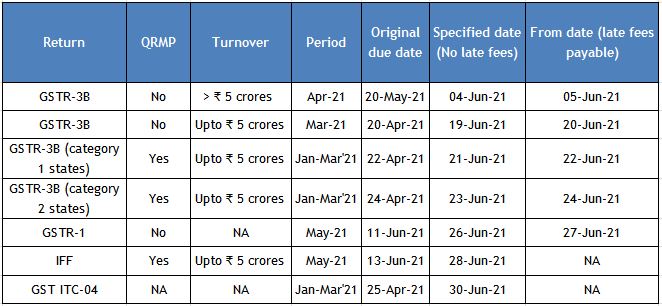
Category 1 States: Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, the Union territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands or Lakshadweep
Category 2 States: Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam, West Bengal, Jharkhand or Odisha, the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Chandigarh or Delhi
SINGAPORE UPDATES
1) MAS launches initiatives under the banner of Accelerating Green Finance
A financial industry taskforce convened by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) launched several initiatives that seek to accelerate the environmentally conscious transformation of the Singaporean financial system.
The Green Finance Industry Taskforce (GFIT) issued a detailed implementation guide for climate-related disclosures by financial institutions. This acts as a framework to help banks assess eligible green trade finance transactions. It has also released a whitepaper on scaling green finance in the real estate, infrastructure, fund management and transition sectors.
The guide sets out best practices that are aligned with the recommendations of the Financial Stability Board’s Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures. It also outlines specific disclosure practices for the insurance, banking and asset management sectors, taking into account the unique features of each. This, MAS said, will help to enhance the quality of FIs’ climate disclosures, and facilitate more consistent and comparable disclosures across FIs.
The taskforce will also launch a series of workshops to build capacity in green finance, targeted at financial institutions and corporates, with support from its industry association partners. These workshops will run from this month until April 2022.
“GFIT’s initiatives to enhance climate-related disclosures and strengthen green capabilities will enable financial institutions to effectively develop green solutions and align their portfolios towards facilitating Asia’s transition to a low carbon economy,” said Gillian Tan, assistant managing director (development and international), MAS.
“These initiatives will also contribute to global efforts to achieve greater consistency and comparability in climate-related disclosures, as well as provide investors and market participants with the necessary information for climate risk analysis and investment decision-making.”
https://abs.org.sg/docs/library/financial-institutions-climate-related-disclosure-document.pdf
https://abs.org.sg/docs/library/fostering-green-finance-solutions-white-paper.pdf
https://abs.org.sg/docs/library/green-finance-industry-taskforce-capacity-building-series.pdf
2) Renewal of Bilateral Swap Arrangement between Japan and Singapore
The Bank of Japan (BOJ), acting as agent for the Minister of Finance of Japan, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) renewed the existing Bilateral Swap Arrangement (BSA) between the two countries on 21 May 2021.
Under the arrangement, authorities in Japan and Singapore can swap their local currencies in exchange for US dollars from each other in times of need, while also enabling Singapore to obtain Japanese yen to meet possible liquidity needs.
The size of the arrangement remains unchanged. Under the terms of the arrangement, Singapore can swap Singapore dollars for up to US$3 billion or its equivalent in Japanese yen from Japan. Japan can swap Japanese yen for up to US$1 billion from Singapore.
The renewal of the BSA incorporates amendments to align the BSA with the recent amendments to the Chiang Mai Initiative Multilateralization (CMIM) Agreement, including the increase in the IMF De-linked Portion from 30% to 40%.
The IMF De-linked Portion represents the amount each member may request from the CMIM when there is no matching IMF supported programme.
BOJ and MAS say the continued bilateral financial cooperation will “contribute to financial stability in both countries, and support growing bilateral economic and trade ties”.
3) MAS Commits over S$42 million to Spur Tech Solutions for Risk Management and Regulatory Technology
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has announced a new Regulatory Technology (RegTech) grant scheme and enhancement of the Digital Acceleration Grant (DAG) scheme. MAS will commit S$42 million for the RegTech grant scheme and DAG scheme.
The RegTech grant scheme, which is available to Singapore-based financial institutions (FIs), aims to promote the adoption and integration of technology solutions in the risk management and compliance functions of FIs. This will help FIs enhance processes and capabilities in these domains and encourage a vibrant RegTech ecosystem in Singapore.
The grant scheme will cover two tracks.
Under the pilot track, FIs can seek funding to pilot potential RegTech solutions before embarking on full-scale integration of the product into its operating environment. Funding for this track will be capped at S$75,000.
Through the production level project track, FIs can seek funding to develop larger scale customised projects that can be fully integrated into the FI’s systems. Funding for such projects will be capped at S$300,000.
Both tracks can be used to support either in-house development or commercial partnerships with RegTech firms based in Singapore.
The DAG was launched in April 2020 to help smaller FIs and FinTech firms adopt digital solutions to better cope with the impact of COVID-19, and to position themselves for subsequent recovery and growth. As of 31 March 2021, MAS received over 1,100 applications from both FIs and FinTech firms. Applicants have tapped on the DAG to adopt cloud solutions and services, online communication and collaboration tools, data-analytics solutions, compliance solutions, and office productivity tools.
In view of the strong response, MAS will commit an additional S$30 million to the DAG till 31 December 2021 to encourage the industry to adopt digital solutions that enhance productivity, cyber security, and operational efficiency. This brings the total grants available under the DAG scheme to S$65 million. Eligibility for the DAG will be extended to life insurance and general insurance agencies that employ not more than 200 agents and employees.
4) MAS consults on revisions to corporate governance guidelines for designated financial holding companies, banks, direct insurers, reinsurers, and captive insurers
On 7 May 2021, The Monetary Authority of Singapore (“MAS”) released a consultation paper setting out its proposed revisions to the Guidelines on Corporate Governance for Designated Financial Holding Companies, Banks, Direct Insurers, Reinsurers and Captive Insurers which are incorporated in Singapore (“CG Guidelines”). The consultation closes on 18 June 2021.
The Guidelines on Corporate Governance comprises principles and provisions of the Code of Corporate Governance which apply to all financial institutions within scope and some additional guidelines for Singapore incorporated financial institutions. The current Code of Corporate Governance was revised in 2018 to reinforce board competencies and place greater emphasis on disclosures of relationship between remuneration and value creation. The revision also increased focus on the interests of stakeholder groups other than shareholders.
The consultation paper proposes to revise the Guidelines on Corporate Governance to incorporate 2018 changes to the Code of Corporate Governance as well as international standards and industry best practices.
Proposed Revisions to the Code of Corporate Governance
Greater responsibilities for board of directors
There is greater emphasis on expected roles and responsibilities of board of directors as set out in the Basel Committee of the Banking Supervision Core Principles for Effective Banking Supervision and the International Association of Insurance Supervisors Core Principles. The Board is expected to review financial institutions corporate governance framework, culture and conduct framework, business objectives and strategies on an annual basis. There is a requirement to have an appropriate risk management system and adequate internal controls to support the financial institution’s risk appetite.
Recommendations for oversight of remuneration practices
The Guidelines on Corporate Governance sets out recommendations for remuneration practices. It is expected that financial institutions design and implement appropriate remuneration policies for employees with active oversight and monitoring of effectiveness of policies by senior management. Effective oversight includes ensuring performance evaluation and conducting independent annual reviews which must take into account both financial and non-financial factors.
Documentation for unresolved concerns of independent directors
As part of the Guidelines on Corporate Governance, MAS requires unresolved concerns for independent directors, particularly those on the running of the company, be documented in the minutes of the board meetings. MAS proposes to include this expectation as a new additional guideline under the Guidelines on Corporate Governance.
Appointment of non-directors to the Board Risk Committee
The Board Risk Committee of a financial institution has statutory responsibilities under the Corporate Governance regulations for overseeing the establishment and operation of an independent risk management system for the financial institution, as well as ensuring the adequacy of the risk management function of the financial institution. To achieve this, the financial institutions, as part of Guidelines on Corporate Governance, are expected to appoint independent directors with skills and competency relevant to their business strategies and objectives. Given the limited pool of resources, some financial institutions have resorted to utilising subject matter experts in their place. MAS proposes that an expert, who is not a director, may be appointed as a member of the Board Risk Committee. Appropriate notifications must be provided to MAS and the individuals must commit to appropriate undertakings for proper accountability.
The consultation paper is available on the MAS website www.mas.gov.sg
5) Singapore and Serbia Sign Avoidance of Double Taxation Agreement
Singapore and Serbia have signed the Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Singapore and the Government of Republic of Serbia for the Elimination of Double Taxation with respect to Taxes on Income and the Prevention of Tax Evasion and Avoidance (“DTA”).
The DTA was signed by Minister for Education and Second Minister for Finance, Mr Lawrence Wong, and Minister of Finance for Serbia, Mr Siniša Mali.
The DTA clarifies the taxing rights of both countries on all forms of income flows arising from cross-border business activities, and minimises the double taxation of such income. This will lower barriers to cross-border investment and boost trade and economic flows between the two countries. Key terms of the Agreement can be found in the Annex.
Article in the DTA | Key terms in the DTA |
Article 5, Permanent Establishment | · Period test of 12 months for construction-related activities, beyond which residents of a contracting state could trigger a taxable presence in the other contracting state; · Threshold of 270 days in any 12-month period for the furnishing of services by an enterprise of a contracting state within the other contracting state |
Article 10, Dividends | · 5% withholding tax rate (if shareholding ≥ 25%); · 10% withholding tax rate (all other cases) |
Article 11, Interest | · 10% withholding tax rate |
Article 12, Royalties | · 5% or 10% withholding tax rate depending on the nature of the royalties |
IRAS- Due dates
Form C-S/C for the FY 2020 -30 – November 2021
Estimated Chargeable Income (ECI) (March year-end)- 30 – June 2021
GST Return for Quarter ending: June 2021- 31 – July 2021