DIRECT TAX
Circulars/Notifications/Press Release
Jeevan Akshay-VII Plan eligible for 80C Deduction
- The Central Government notifies Jeevan Akshay-VII Plan of the Life Insurance Corporation of India as an ‘Annuity Plan’ for Section 80C from AY 2021-22 onwards.
E-Verification Scheme, 2021
- A new scheme called the E-Verification scheme has been notified to facilitate faceless collection of information.
Relaxation in E-verification
- For ITRs filed electronically without a digital signature and not verified by way of EVC or physical dispatch of ITR-V for AY 2020–21, CBDT has given a one-time extension till 28 Feb 2022 to provide such verification.
CBDT prescribes Faceless Appeal Scheme 2021
- CBDT has notified a revised Faceless Appeal Scheme, 2021 with effect from 28 Dec 2021.
- New scheme grants oral hearings to taxpayers through video conference as a matter of right while dealing with their appeals and removes the requirement of draft order as required by the older scheme.
Case Laws
Reliance Telecom Limited / Reliance Communication Limited
- In this case, SC held that ITAT could only rectify any mistake apparent from record and cannot revisit its earlier order and go into the merits. SC observes that ITAT’s order recalling its original order was beyond the scope and ambit of the powers.
Chander Mohan Lall
- In this case, Delhi ITAT has held that Legal fees paid by Indian lawyer to non-residents is in the nature of professional fees and is distinct from FTS. Hence, TDS was not required to be deducted.
M. Abdul Zahid
- In this case, Karnataka High Court has disallowed the purchase expense of assessee carrying iron ore business without necessary approvals. Idea behind the pronouncement was to discourage the business and profession that are carried on illegally.
Jetha Properties Private Limited
- In this case, Bombay High Court has held that expenses incurred for raising floor height of warehouse to secure goods from rainwater is revenue in nature as the said expenditure has been incurred in order to preserve and maintain an already existing asset and it is integral part of the profit-making process and thus revenue in nature.
Elymer International
- ITAT held that in case of bank guarantee issued by a bank, there was no principal-agent relationship between the bank and the assessee which was a mandatory condition for invoking Section 194H. Bank guarantee commission is in the nature of interest u/s 2(28A) and exemption provided u/s 194A(3)(iii) was available to the assessee. Thus, held that no disallowance can be made.
Bekaert Industries Private Limited
- Assessee carries on the business of IT support services with related party. AO disallowed IT support services fee for failure to deduct TDS.
- Upon appeal, ITAT held that use of IT infrastructure constitutes ‘use of industrial equipment’ u/s 9(1)(vi) and DTAA. ITAT further highlighted that SC ruling in case of Engineering Analysis was being applicable only to copyright royalty and not to industrial royalty.
- ITAT further held that payment constitutes industrial royalty as per India-Belgium DTAA and confirmed disallowance for failure to deduct TDS.
Petronash FZE
- In this case, Non-resident Assessee entered into contract with ONGC for executing a turnkey project towards offshore drilling platforms and carried out activities of design and engineering at offshore centres.
- The AO held that 25% of such turnkey revenue was taxable in India which was further reduced to 10% by DRP after considering provisions of Sec. 44BB.
- Considering Assessee’s arguments that none of the activities relating to the project were carried out in India, ITAT thus held that provisions of 44BB do not override the provisions of Section 4 and Section 5 and held no income from the turnkey project is taxable in India.
Suresh Bansal
- Assessee was subjected to search and seizure whereby jewellery was found, but no documentary evidence was produced by the Assessee to the extent of 295.1 grams. Therefore, AO made addition to the Assessee’s income.
- On appeal, CIT(A) allowed a credit for 100 grams of jewellery.
- On further appeal, ITAT deletes additions made on account of 295 grams of jewellery unearthed in a search operation. ITAT followed Instruction No. 1916 which permits presumption of 500gms of jewellery, Gujarat HC ruling in the case of Ratan Lal Vyaparilal Jain and co-ordinate ruling in the case of Satya Bhalla.
Coursera Inc.
- The Assessee had applied for lower deduction certificate (LDC) u/s 197 for 5% on dividend income earned, relying on the most favoured nation clause protocol of India -Switzerland DTAA.
- Department has denied stating that no notification has been issued by the Government of India in this regard and issued 10% deduction certificate u/s 197.
- High Court held that Department cannot refuse to follow binding jurisdictional decision merely on the basis that the Department proposes to file an appeal. Therefore, directed department to issue Lower Deduction Certificate of 5%.
Corporate laws
ECB 2 Return for the month of December 2021 - To be filed on or before 7 January 2022.
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs vide General Circular nos. 19/2021 & 20/2021 dated 8 December 2021 has further extended the relaxation given to companies for holding the Annual General Meetings which were due in the year 2021/Extra-ordinary General Meetings through Video Conferencing (VC) and Other Audio-Visual Means (OVAM) subject to compliance with the prescribed framework. Similar extension has also been granted to Companies to hold AGMs in 2022 for the financial year ending before/on 31 March 2022 through Video Conference (VC) or Other Audio-Visual Means (OAVM) as per respective due dates by 30 June 2022 (General Circular No. 21/2020) dated 14 December 2021.
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs vide General Circular no 22/2021 dated 29 December 2021, has granted further extension till 15 February 2022 for filing of Forms AOC-4, AOC-4 (CFS), AOC-4 (XBRL), AOC-4 non-XBRL and up to 28 February 2022 for filing of MGT-7/MGT-7A and no additional fees will be levied upon.
Goods and Services Tax
Supreme Court of India restores its earlier order extending due dates for filing appeals/petitions
In March 2020, the Supreme Court of India in its suo motu writ petition no. 3/2020 dated 23 Mar 2020 ordered that a period of limitation under general law of limitation or under special laws (both Central and/or State) shall stand extended with effect from 15 Mar 2020 till further order/s to be passed by the Hon’ble Supreme Court. Thereafter, considering that the country is returning to normalcy, the Supreme Court disposed of the aforesaid suo motu proceedings by restricting the extension till 2 Oct 2021.
Now considering the rapid increase in number of Covid cases across the country and spread of the new variant of virus, the Supreme Court has restored its earlier order dated 23 Mar 2020 and has directed that the period from 15 Mar 2020 till 28 Feb 2022 shall stand excluded in computing period of limitation as prescribed under any general or special laws, in respect of all judicial or quasi-judicial proceedings. In cases where the limitation period would have expired during the period from 15 Mar 2020 to 28 Feb 2022, then limitation period of 90 days would be available from 1st March 2022, notwithstanding the actual balance period of limitation remaining. In case the actual balance period of limitation as on 1 Mar 2022 is greater than 90 days, then that longer period shall apply.
This will be applicable for any petition / application / suit / appeal / all other proceedings before Supreme Court / High Courts / Tribunals and Statutory Authorities.
Reimbursement of electricity and water charges by tenant to landlord liable to GST – Maharashtra AAR
The Maharashtra AAR in the case of M/s Indiana Engineering Works (Bombay) Pvt. Ltd. has held that the recovery of electricity and water charges at actuals from the tenant is integral part of monthly license fees and thus, GST is applicable on such charges. The Advance Ruling authority on a perusal of the provisions of the Maharashtra Rent Control Act, 1999 noted that provision of electricity and water by the landlord is an essential supply for effective enjoyment of the rented premises without which occupation of the premises would not be possible. Further, the AAR also held that the Applicant in the present case does not act as Pure Agent of the tenant since it is the primary responsibility of the Applicant to pay for electricity and water charges to respective agencies and even after the tenant leaves the premises, the main electric and water meter is going to remain in the name of the Applicant.
No GST on amount recovered from employees towards transport facility provided to them – Maharashtra AAR
The Maharashtra AAR in the case of M/s Integrated Decisions and Systems India Pvt. Ltd. has held that GST is not payable on amount recovered from employees towards transport facility provided to them. The AAR in this case noted that the Applicant is engaged in the business of providing software development and support services to its parent company located outside India and as a welfare, safety and security they are providing transport facility to its employees. The AAR held that, arranging transport facility for its employees is neither incidental / ancillary to software development nor is in the course or furtherance of business of software development. Further, the AAR observed that GST is already discharged on the gross value of bills raised by the third party vendors who provide “renting of motor vehicle service”, “cab service” to the Applicant and the amounts recovered by the Applicant from employees are nothing but part of the amount paid to such third party vendors which has already suffered GST.
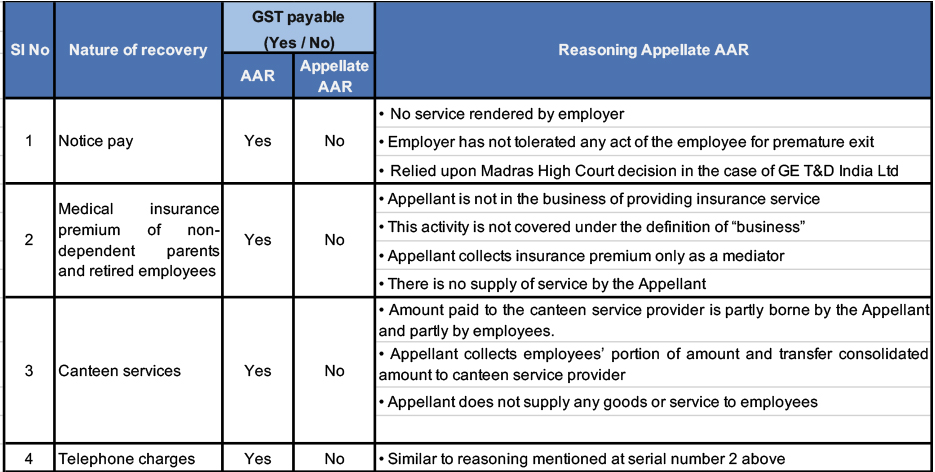
Taxability of employee recoveries – Madhya Pradesh Appellate AAR overrules AAR
In our last month’s newsletter, we had covered ruling of Madhya Pradesh AAR in the case of M/s Bharat Oman Refineries Limited in which the AAR held that GST is leviable on various recoveries from employees such as notice pay recovery, medical insurance premium of non-dependent parents and retired employees, canteen recovery and telephone charges recovery. The Applicant aggrieved by this Ruling went into appeal before Appellate AAR who has overruled the ruling of AAR. For ease of reading, we have explained in table below the reasoning adopted by the Appellate AAR:
SEZ Unit liable to pay GST under RCM – Maharashtra AAR
The Maharashtra AAR in the case of M/s Portescap India Private Limited has held that SEZ unit is liable to pay GST under reverse charge mechanism (RCM) on renting of immovable property services received from SEZ Developer viz. SEEPZ, Mumbai which is a local authority. The AAR in support of its conclusion noted that Section 16 of the Integrated GST Act, 2017 deals with zero-rated supply and Section 16 is applicable only to a supplier of goods or services and not to a recipient. Therefore, with respect to the services which are notified under RCM, SEZ unit which is recipient is not eligible for zero-rated benefit and it has to pay GST under RCM. The AAR also noted that Section 26 of the SEZ Act which deals with exemption from duties and taxes is not yet aligned with GST law, as Section 26 does not cover exemption from Central GST or State GST or Integrated GST. Thus, the AAR noted that Section 26 of SEZ Act cannot be referred to decide taxability under GST law.
Government makes 100% invoice matching mandatory to claim input tax credit from 1 January 2022
It is common knowledge in GST that the recipient can claim input tax credit only if the supplier has paid GST to the Government. However, with effect from 1 Jan 2022, invoice matching has been made mandatory for the recipient to claim input tax credit. Meaning, the supplier needs to report the Tax Invoice in his GSTR-1 return and the same needs to be populated in GSTR-2B report of the recipient in order for the recipient to claim the credit.
Government extends due date to file GST annual return by two months
The due date to file GST Annual Return in Form GSTR-9 and Reconciliation Statement in Form GSTR-9C for the financial year 2020-21 is extended by two months to 28 Feb 2022. Form GSTR-9 is required to be filed by taxpayers having their aggregate turnover above INR 2 crores and Form GSTR-9C is applicable for those taxpayers having their aggregate turnover above INR 5 crores. The original due date to file these forms was
31 Dec 2021.
Government extends last date for submitting applications for export incentive scheme by one month
The Government has extended the last date to file online applications for scrip-based export incentive schemes viz. MEIS, SEIS, 2% additional ad hoc incentive, RoSCTL by one month to 31 Jan 2022. It may be noted that, applications not submitted by this date would become time-barred and late cut provisions would not be available.
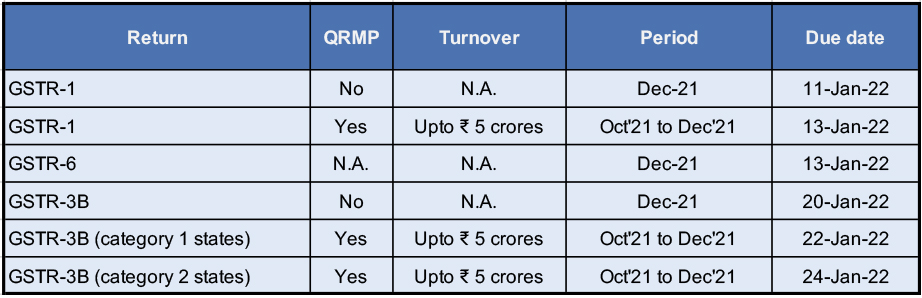
Due Dates
GST Compliance calendar for due dates falling in the month of January 2022
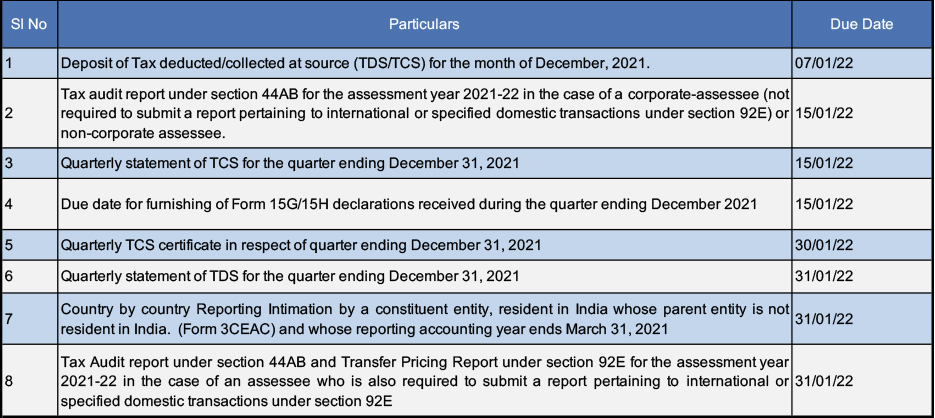
Important Due Dates
SINGAPORE UPDATES
Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA)
1) Public Consultation on Proposed Legislative Amendments Relating to Data, Digitalisation and Corporate Transparency for a Trusted and Vibrant Business Environment in Singapore
Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) is conducting a public consultation on proposed amendments to the Companies Act, Accountants Act, Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority Act, Business Names Registration Act, Limited Liability Partnerships Act (“LLP Act”), Limited Partnerships Act and Variable Capital Companies Act 2018 on matters relating to data accuracy and privacy, digitalisation of correspondence and corporate transparency. The public consultation exercise will run from 17 December 2021 to 28 January 2022.
ACRA regularly reviews and seeks public feedback on legislation to foster a trusted and vibrant business environment in Singapore. Following its public consultation on proposed amendments to the CA in July 2020, ACRA is proposing additional amendments to the CA as well as other ACRA-administered legislation. The proposed amendments are to:
- empower ACRA to draw data from other agencies or entities to improve filing convenience and data accuracy;
- strike a balance between corporate transparency and personal data privacy;
- facilitate digital correspondences with businesses to improve efficiency and support sustainability efforts;
- enhance transparency of beneficial ownership of companies and limited liability partnerships (“LLPs”) to maintain Singapore’s reputation as a trusted financial hub; and
- streamline processes for service of summons and striking off to facilitate compliance.
Improving filing convenience and data accuracy
As the national business registry, one of ACRA’s functions is to collect documents and information on business entities and related individuals, and public accountants, and to provide the public access to such information to enhance corporate transparency and facilitate business activity. The proposed amendments empower ACRA to:
- obtain data from specified government agencies for the purpose of filing; and
- use data from specified entities to verify information on ACRA’s
This will reduce the amount of data customers must file with ACRA, improve convenience to filers, and improve the accuracy and value of the data to users. It will also facilitate Government-to-Business digital correspondences with business entities.
Balancing corporate transparency and personal data privacy
ACRA seeks to strike a balance between corporate transparency and personal data privacy and to address concerns that individuals may have over the disclosure of the personal data that they file with ACRA. ACRA has received feedback that it should limit the personal data that is made available publicly, and at the same time, there have been requests from government agencies and private institutions for ACRA to share more business data for research, enforcement, and verification purposes.
The proposed amendments seek to:
- provide flexibility for ACRA to specify personal data relating to individuals that may need to be collected and to introduce a tiered disclosure framework to calibrate the disclosure of personal data;
- standardise the references to the “name” of individuals in ACRA-administered legislation;
- partially mask the identification numbers of all individuals in ACRA’s registers which are made available to the public; and
- introduce a “contact address” as the default address of individuals that will be shown to the public, instead of the individual’s residential
Enhancing transparency of beneficial ownership of companies and LLPs
ACRA continues to improve the transparency of beneficial ownership of companies and LLPs and reduce opportunities for the misuse of corporate entities for illicit purposes. The proposed amendments are to:
- remove the exemption of certain local companies from the requirement to maintain registers of nominee directors;
- require companies and LLPs to verify the accuracy of information in their register of controllers with their controllers annually;
- introduce a financial penalty of up to S$10,000 on any person who inadvertently, or without intent to mislead or defraud, makes any inaccurate or erroneous statement or information on beneficial ownership to the Registrar under the CA and LLP Act;
- increase the maximum fine for offences pertaining to the registers of controllers and nominee directors from S$5,000 to S$20,000; and
- extend the prescribed time for companies and LLPs to update their register of controllers from two business days to seven calendar
These measures are part of the ongoing efforts to maintain Singapore’s strong reputation as a trusted financial hub and are in line with international standards for combating money laundering, terrorism financing and other threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
Streamlining and clarifying processes
Other proposed amendments to the CA and other ACRA-administered legislation aim to clarify and update regulatory requirements, and they include, to:
- standardise and consolidate the service of summons and other civil originating process under the Acts administered by ACRA;
- streamline and clarify the striking off regime for companies, foreign companies, variable capital companies and LLPs; and
- make it clear that the Registrar may update the register of directors based on bankruptcy information provided by the Ministry of Law.
2) ACRA Suspends Registered Qualified Individual R Shanmugaratam for False Information Filed with ACRA
Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) has suspended the registration of Registered Qualified Individual (RQI) of former director of accounting firm Citadelle Corporate Services R Shanmugaratam for 12 months from 11 December 2021 to 10 December 2022, for providing false information in an annual return filed with ACRA.
ACRA had investigated Shanmugaratam in connection with the annual return filed for YO54 Holdings Pte Ltd (YO54) on 27 February 2018. In the annual return, Shanmugaratam declared that he had verified with the director of YO54 that the company qualified as a small and dormant company under the Companies Act for Year of Assessment 2017. However, Shanmugaratam had in fact not verified this with the director.
An RQI is an individual who provides corporate secretarial services for business entities and transacts with ACRA on behalf of his/her clients. The services provided by RQIs include helping clients to file annual returns and/or fulfil the requirements under the Companies Act or other Acts under ACRA’s purview. RQIs must be registered with ACRA and fulfil general requirements such as being a fit and proper person before providing corporate secretarial services.
RQIs must ensure that filings with ACRA are carried out in accordance with instructions from their clients, and that the filings are true and accurate. RQIs found to have breached their obligations could face financial penalties of up to $10,000 per breach and/or have their registration suspended or cancelled.
Monetary Authority of Singapore and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore Updates
1) MAS Proposes to Introduce Due Diligence Requirements for Corporate Finance Advisers
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (“MAS”) is proposing to introduce due diligence requirements for holders of a capital markets services (“CMS”) licence and banks, merchant banks and finance companies exempt from holding a CMS licence that undertake the regulated activity of advising on corporate finance (“CF advisers”), in a move to improve industry standards and raise the minimum standards of conduct of CF advisers, strengthen public confidence and promote informed decision making by investors through quality disclosures.
The proposed requirements set out the minimum standards which CF advisers should adhere to when conducting due diligence on CF transactions. Part I (General Requirements) of the Notice sets out general requirements which apply when CF advisers advise on corporate finance, while Part II (Listing Applicants) sets out additional requirements for CF advisers acting as issue managers (“IMs”) for initial public offerings (IPOs) on the Singapore Exchange Securities Trading Limited (“SGX-ST”) or reverse takeovers and very substantial acquisitions entered or to be entered into by an entity listed on the SGX-ST.
An outline of the key proposed requirements under the new Notice is set out below.
General due diligence requirements
Implementing policies, procedures and controls: A CF adviser must develop and implement policies, procedures and controls to meet all the requirements of the Notice, monitor the implementation and periodically consider the need to enhance such policies, procedures and
Acting with due care, skill and diligence: A CF adviser must act with due care, skill and diligence including exercising reasonable judgement in determining the nature and extent of due diligence work to be performed for a transaction and assessing the accuracy and completeness of representations and information made or given by its customer and conducting the appropriate verification of such
Managing conflicts of interest: A CF adviser must, among other things, identify, mitigate and disclose to its customers potential, actual or perceived material conflicts of interest between the interests of its customers and those of the CF adviser or its related corporation. Where a CF adviser or its related corporations also conduct other activities in relation to the offering process (e.g. issue of research reports) it must, among other things, have in place controls for that other activity. Further, the CF adviser must put in place effective safeguards to prevent the disclosure of confidential or price sensitive information by its directors, employees, or representatives or other agents who receive such information when advising on corporate finance, to personnel carrying on other
Governance and supervision: There must be an adequate framework for senior management (the person principally responsible for the day-to-day management of the relevant functions which advise on corporate finance) to have oversight over matters including acceptance of an engagement to act as a CF adviser, appointment of the transaction team, and the proposed due diligence plan for each specific The CF adviser must also ensure adequate supervision of the performance of the representatives who advise on corporate finance, including their performance of due diligence work for each specific transaction. Matters such as material issues relating to non-compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements, conflicting information from a customer or other persons, suspicious circumstances and material issues that may be prejudicial to the transaction must be reported to senior management and there must be clear reporting lines to escalate such reportable matters.
Keeping records: A CF adviser must prepare, maintain and retain records of all data, documents and information that it is required to obtain or produce to meet the requirements under the Notice.
Additional due diligence requirements for CF advisers acting as IMs
- Advising listing applicant on regulatory requirements: Subject to the terms of the agreement between the CF adviser and its customer, a CF adviser must advise and guide listing applicants (including its manager or trustee-manager, where applicable) and their directors as to their duties and responsibilities under the Securities and Futures Act and listing rules and other relevant regulatory.
2) Singapore-Armenia Agreement for the Avoidance of Double Taxation Enters into Force
The Agreement between the Government of the Republic of Singapore and the Government of the Republic of Armenia for the Elimination of Double Taxation with respect to Taxes on Income and the Prevention of Tax Evasion and Avoidance (“DTA”), signed on 8 July 2019, entered into force
on 23 December 2021.
The DTA will benefit businesses in both Singapore and Armenia as well as boost bilateral trade and investment flows between the two countries.
OTHER UPDATES
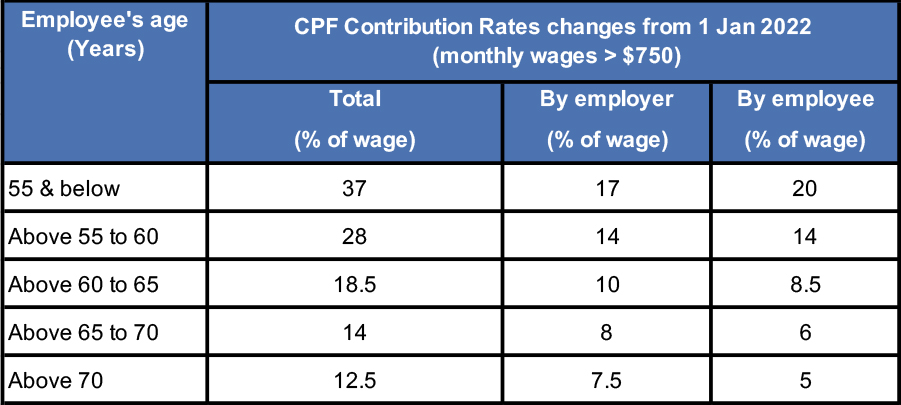
1) Increase in CPF contribution rates from 1 January 2022
Singapore will increase the Central Provident Fund (CPF) contribution rates for employees aged 55 to 70 years from 1 January 2022.
The increase in the CPF contribution rates will be fully allocated to the employees’ Special Account to provide a bigger boost to their retirement income.
For those earning monthly wages of more than $500 to $750, the employee contribution rates will continue to be phased in.
There are no changes to the graduated contribution rates for first and second year Singapore Permanent Residents (SPRs).
The following table summarises the contribution rates for Singapore Citizens and SPRs (from third year and onwards) from 1 January 2022.
2) Competition regulators in Singapore and the Philippines sign MOU on corporation in enforcement of Competition Law
The Competition and Consumer Commission of Singapore (“CCCS”) and the Philippine Competition Commission (“PCC”) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding on Implementation of Competition Law (“MOU”) to establish a framework for corporation for the effective enforcement of competition laws in Singapore and Philippines.
The MOU states that CCCS and PCC will promote competition by addressing anti- competitive activities to facilitate the development and operation of well-functioning markets in their respective countries. CCCS and PCC will cooperate with and provide assistance to each other to the extent consistent with the laws and regulations in force in their respective countries, their respective important interests, and reasonably available resources.
The MOU will facilitate the exchange of information between CCCS and PCC, as well as enforcement of coordination for cases of mutual interest.
https://www.cccs.gov.sg/media-and-consultation/newsroom/media-releases/cccs-pcc-sign-mou-2021
IRAS- Due Dates
- Estimated Chargeable Income (ECI) for December 2021 year end: 31 March 2022
- GST Return: For the Quarter ended December 2021: 31 January 2022
- Form C-S for Dec 2021 year end: 30 November 2022